Contents
- PyQt5 Tutorial - 파이썬으로 만드는 나만의 GUI 프로그램
- 1. PyQt5 소개 (Introduction)
- 2. PyQt5 설치 (Installation)
- 3. PyQt5 기초 (Basics)
- 4. PyQt5 레이아웃 (Layout)
- 5. PyQt5 위젯 (Widget)
- QPushButton
- QLabel
- QCheckBox
- QRadioButton
- QComboBox
- QLineEdit
- QLineEdit (Advanced)
- QProgressBar
- QSlider & QDial
- QSplitter
- QGroupBox
- QTabWidget
- QTabWidget (Advanced)
- QPixmap
- QCalendarWidget
- QSpinBox
- QDoubleSpinBox
- QDateEdit
- QTimeEdit
- QDateTimeEdit
- QTextBrowser
- QTextBrowser (Advanced)
- QTextEdit
- QTableWidget
- QTableWidget (Advanced)
- 6. PyQt5 다이얼로그 (Dialog)
- 7. PyQt5 시그널과 슬롯 (Signal&Slot)
- 8. PyQt5 그림 그리기 (Updated)
- 9. PyQt5 실행파일 만들기 (PyInstaller)
- 10. PyQt5 프로그램 예제 (Updated)
- ▷ PDF ebook
Tutorials
- Python Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- PyQt5 Tutorial
- BeautifulSoup Tutorial
- xlrd/xlwt Tutorial
- Pillow Tutorial
- Googletrans Tutorial
- PyWin32 Tutorial
- PyAutoGUI Tutorial
- Pyperclip Tutorial
- TensorFlow Tutorial
- Tips and Examples
이벤트 핸들러 재구성하기2¶
이번에는 mouseMoveEvent를 이용해서 마우스의 위치를 트래킹해서 출력해보겠습니다.
예제¶
## Ex 7-4. 이벤트 핸들러 재구성하기2.
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel
class MyApp(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
x = 0
y = 0
self.text = 'x: {0}, y: {1}'.format(x, y)
self.label = QLabel(self.text, self)
self.label.move(20, 20)
self.setMouseTracking(True)
self.setWindowTitle('Reimplementing event handler')
self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 200)
self.show()
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):
x = e.x()
y = e.y()
text = 'x: {0}, y: {1}'.format(x, y)
self.label.setText(text)
self.label.adjustSize()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = MyApp()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
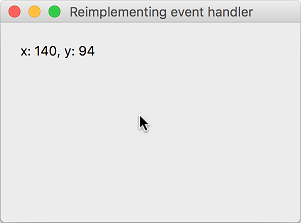
위젯 안에서 마우스를 움직이면 이벤트가 발생하고, 재구성한 이벤트 핸들러를 통해 마우스의 위치를 출력합니다.
설명¶
self.text = 'x: {0}, y: {1}'.format(x, y)
self.label = QLabel(self.text, self)
self.label.move(20, 20)
x, y의 값을 self.text로 저장하고, self.label의 텍스트로 설정합니다.
위치를 x=20, y=20 만큼 이동해줍니다.
self.setMouseTracking(True)
setMouseTracking을 True로 설정해주면, 마우스의 위치를 트래킹합니다.
디폴트는 setMouseTracking(False) 상태이며, 마우스 버튼을 클릭하거나 뗄 때만 mouseEvent가 발생합니다.
def mouseMoveEvent(self, e):
x = e.x()
y = e.y()
text = 'x: {0}, y: {1}'.format(x, y)
self.label.setText(text)
self.label.adjustSize()
이벤트 e는 이벤트에 대한 정보를 갖고 있는 하나의 객체입니다. 이 이벤트 객체 (event object)는 생성된 이벤트의 유형에 따라 다릅니다.
e.x(), e.y()는 위젯 안에서 이벤트가 발생했을 때 마우스 커서의 위치를 반환합니다.
만약 e.globalX(), e.globalY()로 설정해주면, 화면 전체에서 마우스 커서의 위치를 반환하게 됩니다.
self.label.adjustSize() 메서드로 라벨의 크기를 자동으로 조절하도록 합니다.
이전글/다음글
이전글 : 이벤트 핸들러 재구성하기
다음글 : 사용자 정의 시그널